Sometimes it is easy to figure out food sensitivities – especially when they only involve one food or one kind of symptom. For example, lactose intolerance (a type of enzymatic food intolerance where people are deficient in the enzyme needed to digest milk sugar) is related only to milk and milk products, so it’s easy to notice the gastrointestinal symptoms after a nice bowl of ice cream with the kids. But other sensitivities are not so obvious.
Take pharmacological food intolerance, or just ‘food intolerance.’ This type of food sensitivity has always been hard to pin down, on both an individual level and in clinical studies. Symptoms can arise hours or even days after you eat a trigger food, and their severity depends on how much you ate, whether you ate any other trigger foods in prior days, and if you have other health conditions or environmental sensitivities. Furthermore, your symptoms may be different from those of someone else who reacts to the same foods.
On top of this, food intolerance is a reaction to chemicals that are found in a wide variety of foods. For example, if you were sensitive to histamine, you would need to watch out for fruits, meats, cheeses, chocolate, etc. If you were sensitive to artificial colors and preservatives, you would need to read every food label. This is different than food allergies, where people are oversensitive to the proteins found in specific foods. With food intolerance, your food journal wouldn’t be tracking the foods as much as the chemicals inside them. And that’s when things start to fall into place, because, as we’ll see, your symptoms aren’t always caused by the last thing that you ate.
More information: Common food triggers
How food intolerance works
The term ‘pharmacological food intolerance’ underscores the idea that foods, no matter how natural, can contain chemical compounds that are foreign substances in our bodies (like benzoate in fruit or artificial colors in yogurt) or excess amounts of chemicals that our bodies normally produce (like tyramine or histamine in certain cheeses). These chemicals are referred to as xenobiotics, a term which also covers substances like medications, poisons, and environmental pollutants that enter our bodies. This means that pharmacological food reactions share characteristics that are already familiar to us from our experiences with other xenobiotics. In food intolerance:
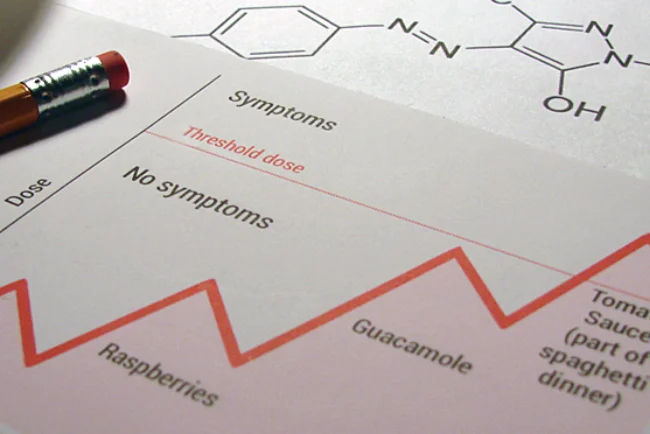
- The severity of your reaction depends on the dose. Below the threshold dose, no symptoms are observed.
- Doses are additive across multiple meals. What you ate throughout the day, and even the previous day, counts towards your accumulated dose. Symptoms occur when the accumulated dose exceeds the threshold dose.
- Multiple food chemicals can work together to exacerbate the effects of the others.
- Withdrawal symptoms can occur.
- You can become temporarily tolerant of a food chemical.
The most important of these ideas is the concept of a threshold dose. If you are very sensitive to a food chemical, you have a low threshold, and a small amount is all that is needed to produce symptoms. If you have a high threshold, eating small amounts of a substance will not produce any symptoms. And it’s not necessary to consume all of your food chemical in one meal in order to exceed the threshold dose – little bits can add up over a couple of days. If you were looking to see which food caused your symptoms, you might find that it was several foods over several meals that all contained the same trigger chemical.
In general, we can say that food intolerant people have lower dose thresholds than the rest of the population since most people do not react to food. This is partly due to differences in how well the body can rid itself of chemicals and partly due to how susceptible one is to experiencing adverse reactions – this is all part of the natural variations among people. However, it turns out that your personal threshold dose can also vary over time, depending on what else you have eaten, what medications you have taken, and other health-related factors.
An example of accumulated and threshold doses

Consider the chart on the right that tracks meals over four days – simplified, of course, for a hypothetical person. If you experienced symptoms on Day 4, would your first inclination be to blame the spaghetti dinner and perhaps the gluten-containing pasta in particular?
Our hypothetical person is actually sensitive to salicylate and amines, and she needs a mix of both to see symptoms – it turns out that honey, raspberries, guacamole, and tomato sauce all contain at least one of these chemicals. The chemicals accumulated in her body over the course of three days until her threshold dose (which, luckily for her, is rather high) was exceeded on the fourth day.
Our person had wondered about gluten sensitivity in the past, but didn’t seem to react reliably to wheat. Now that she is mindful of her trigger chemicals and her threshold dose, she can eat some of the foods she likes without adverse effects.
© 2014 FoodConnections. All rights reserved.
FoodConnections.org – The science-based food intolerance resource since 2013
Bibliography
Loblay R, Swain AR. Food Intolerance. In: Wahlqvist ML, Truswell AS, editors. Recent Advances in Clinical Nutrition. London: Libbey; 1986. p. 169–77.
Swain AR, Soutter VL, Loblay RH. RPAH elimination diet handbook. Rev. ed. Camperdown, Australia: Allergy Unit, Royal Prince Alfred Hospital; 2011.